Spatial Views (preview)#
Warning
This feature is in preview and therefore is not feature complete or may have some bugs.
As of Arches version 6.1.0, it is possible to create spatial views of resource instance data that can be consumed by any client that supports PostGIS spatial views.
Currently the preview only allows the spatial views to be created in Django admin by managing the Spatial Views entities.
The spatial views are only able to represent the data in a flattened state, meaning that the data in nested cards are flattened into a single comma separated attribute value, with the card sort order honoured. Therefore, it is important to consider how to attribute the views being created.
Spatial Views Model Schema#
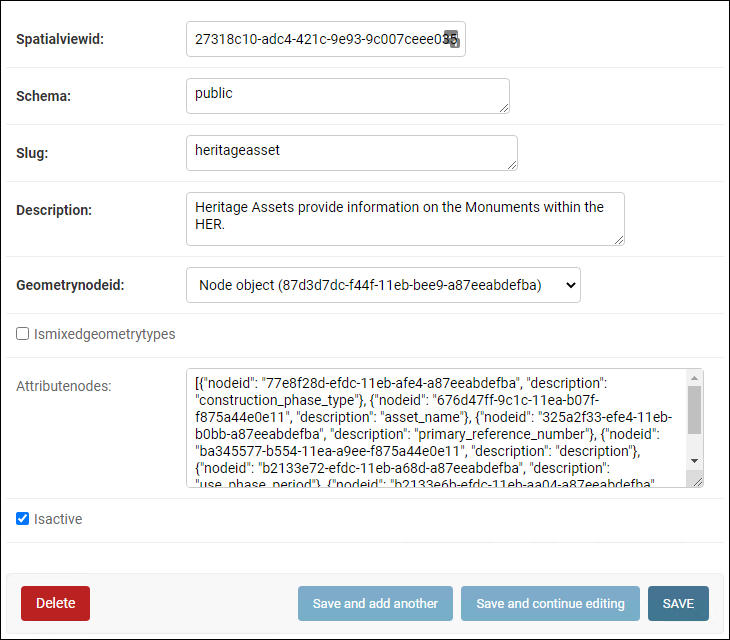
The Spatial View model schema is defined as follows:
- Spatialviewid
Unique identifier for the spatial view.
- Schema
The database schema that the spatial view belongs to.
publicis used by default but if another is used then it must have already been created in the database.- Slug
This is will be joined with the
Schemato form the name of the spatial view. This value must follow slug format of only lower-case letters, numbers, and hyphens. It cannot start with a number.- Description
The text that is added as a comment on the spatial view in the database , which can be accessed as metadata for consuming clients where supported. pg_featureserv for example will present this as the layer description.
- Geometrynodeid
The UUID of the geojson-feature-collection node that underpins the geometry of the spatial view.
- Ismixedgeometrytype
Boolean value that indicates whether the geometry of the spatial view is a mix of different geometry types. This is ideal where the spatial view will be used by a vector tile service.
Default value is
false.- Attributenodes
A JSON object that contains a list of attribute object defining the UUIDs of the nodes that comprise the attributes of the spatial view and a text description of that attribute for metadata.
Note
The name of the attributes are automatically generated from the node name using Postgresql a compliant format.
[ { "nodeid": "77e8f28d-efdc-11eb-afe4-a87eeabdefba", "description": "construction_phase_type" }, { "nodeid": "676d47ff-9c1c-11ea-b07f-f875a44e0e11", "description": "asset_name" }, { "nodeid": "325a2f33-efe4-11eb-b0bb-a87eeabdefba", "description": "primary_reference_number" }, { "nodeid": "ba345577-b554-11ea-a9ee-f875a44e0e11", "description": "description" }, { "nodeid": "b2133e72-efdc-11eb-a68d-a87eeabdefba", "description": "use_phase_period" }, { "nodeid": "b2133e6b-efdc-11eb-aa04-a87eeabdefba", "description": "functional_type" }, { "nodeid": "77e8f29d-efdc-11eb-b890-a87eeabdefba", "description": "cultural_period" } ]
nodeidThe UUID of the node that needs adding. This must be in the same model and the Geometrynodeid.
descriptionThe text description of the attribute, which will be added as metadata.
- Isactive
Boolean value that indicates whether the spatial view is available. When set to
falsethe spatial view is removed from the database, but allows the definition to remain. Setting totruerecreates the spatial view in the database.Default is
true.
Creating your first spatial view#
Django Admin#
SQL Insert#
You can load the spatial view definition into the database using the following SQL:
INSERT INTO public.spatial_views ( spatialviewid , schema , slug , description , ismixedgeometrytypes, attributenodes , isactive , geometrynodeid ) VALUES ( '2a578e84-b21a-431d-8de0-59e4d46a88fb', 'public', 'artefact', 'Defines information relating to the character of man made items of heritage significance as identified by the Portable Antiquities Scheme includes individual artefacts, architectural items, artefact assemblages, individual ecofacts and ecofact assemblages, and environmental samples.', false, ' [{ "nodeid": "c30977b0-991e-11ea-ba04-f875a44e0e11", "description": "description" }, { "nodeid": "dd8032af-b494-11ea-8110-f875a44e0e11", "description": "primary_reference_number" }, { "nodeid": "dd8032b1-b494-11ea-a183-f875a44e0e11", "description": "legacy_id" }, { "nodeid": "99cfe72e-381d-11e8-882c-dca90488358a", "description": "from_date" }, { "nodeid": "22e7c550-afc2-11ea-a4a8-f875a44e0e11", "description": "repository_owner" }, { "nodeid": "50edbf22-ab25-11ea-a258-f875a44e0e11", "description": "storage_area_name" }, { "nodeid": "546b1630-3ba4-11eb-9030-f875a44e0e11", "description": "artefact_type" }, { "nodeid": "5b0dfb27-7fe2-11ea-8ac9-f875a44e0e11", "description": "artefact_name" }, { "nodeid": "99cff7f8-381d-11e8-a059-dca90488358a", "description": "to_date" }, { "nodeid": "99cfffd1-381d-11e8-ab51-dca90488358a", "description": "cultural_period" } ] ', true, 'f7ccc8b9-f447-11eb-9cb1-a87eeabdefba' );
Using the spatial views#
To use the spatial views in your client application or datasource for a service, you will need to configure that client to connect to the database using the following credentials:
host: the hostname of the arches database server
port: the port of the arches database server
database: the name of the arches database
user: arches_spatial_views
password: arches_spatial_views
If you are using a client that requires views to geometry type specific (for example ArcGIS), ensure that you have set Ismixedgeometrytype to false.
Important
Currently it is not possible to use the user/groups permissions to restrict access. You will need to manually create specific database users and assign them to the spatial views.
Example Usage#
pg_featureserv and pg_tileserv are lightweight open source feature and vector tile service providers that can be used with these spatial views.
https://access.crunchydata.com/documentation/pg_featureserv/latest/ https://access.crunchydata.com/documentation/pg_tileserv/latest/
Once you have installed the application to run on your machine, open the config file located at:
/path/to/pg_featureserv/config/pg_featureserv.toml
Set the DbConnection setting to the following and restart the application:
DbConnection = "postgresql://arches_spatial_views:arches_spatial_views@<HOSTNAME>:<PORT>/<DBNAME>"